Diecast vs Resin Cars Understanding the Basics
The world of scale model cars offers a fascinating glimpse into automotive history, engineering, and design. Within this hobby, collectors and enthusiasts often face a fundamental choice diecast vs resin cars. Both represent different manufacturing processes, material compositions, and aesthetic outcomes. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions, whether you’re a seasoned collector or a newcomer. This article explores the top 5 differences between diecast and resin cars, providing insights into their construction, detailing, durability, collectibility, and cost. By understanding these key aspects, you’ll be better equipped to appreciate the nuances of each type and select the models that best suit your preferences and collecting goals. The journey begins with a fundamental understanding of what defines each type of model car.
Diecast Cars Features and Construction
Diecast cars are primarily constructed using a die-casting process, where molten metal (typically zinc alloy, often with small amounts of aluminum and copper) is injected into a mold. This process allows for intricate designs and high levels of detail, making diecast cars a popular choice for collectors. The metal body provides a substantial weight, contributing to a realistic feel, and the manufacturing method enables manufacturers to create detailed features such as opening doors, hoods, and trunks, enhancing the overall appeal. These features, combined with the robust construction, make diecast cars a durable option that can withstand handling and display. The manufacturing process, while complex, allows for mass production, making diecast models generally more affordable and accessible to a wider audience. Collectors often appreciate the tactile feel and the ability to interact with the moving parts, such as the wheels, steering, and doors.
Materials Used in Diecast Cars

The primary material used in diecast cars is a zinc alloy, often referred to as Zamak, which offers a balance of strength, castability, and affordability. This alloy typically includes zinc, aluminum, magnesium, and copper. This alloy composition allows for detailed castings with excellent dimensional accuracy. Other materials include plastic for interior components, tires made of rubber or PVC, and glass or transparent plastic for windows. The combination of metal and plastic provides a realistic look and feel, contributing to the authenticity of the models. The use of high-quality materials is essential for durability and the overall look and feel of the diecast car. These are critical when considering the longevity and value of collectible pieces. The materials are often chosen based on their ability to replicate the look and feel of the real car accurately.
Manufacturing Process of Diecast Cars
The die-casting process begins with creating highly detailed molds. Molten metal is then injected into these molds under high pressure. Once the metal solidifies, the parts are extracted, trimmed, and cleaned. This process allows for complex designs and intricate details. After casting, the parts are often painted and assembled. The painting process can include multiple layers and detailed graphics. The assembly involves attaching various components, such as the interior, wheels, and windows. Diecast car manufacturers employ various techniques, including tampo printing for details like logos and markings. This process is highly efficient and suitable for mass production, making diecast models accessible to a broad audience. The quality of the final product depends heavily on the precision of the molds, the quality of the materials, and the care taken during assembly.
Resin Cars Features and Construction
Resin cars, on the other hand, are typically made using a mold-casting process. Liquid resin is poured into a mold and allowed to cure and harden. Resin cars often allow for greater detail and customization due to the flexibility of the resin material. This construction method also allows for limited production runs, making resin models more exclusive. The resin material is lighter than diecast metal, which is one of the main differences. Resin models usually lack moving parts, and the focus is primarily on the visual appearance and intricate detailing. Resin models are often favored by model enthusiasts who appreciate highly detailed, accurate representations of specific vehicles. The overall design and aesthetic appeal are the primary focus in their construction. The process also offers advantages in detailing, allowing for finer features.
Materials Used in Resin Cars
The primary material used in resin cars is, of course, resin. This can be a variety of thermosetting polymers, which are cured using catalysts or heat. Resin formulations allow for complex shapes and fine details. Other materials include photo-etched parts for grilles and other intricate components, transparent plastic for windows, and various paints and decals for finishing. The composition allows for highly detailed representations. Modelers often use custom paints and finishes to achieve a high level of realism. The materials used must be carefully selected to ensure the final product meets the desired aesthetic and quality standards. The ability to work with a wide range of materials makes resin a versatile option for creating highly detailed and realistic models. The quality of the resin and other materials directly impacts the model’s final appearance.
Manufacturing Process of Resin Cars
The resin manufacturing process involves creating molds, often using a master model or a 3D-printed design. Liquid resin is carefully poured into these molds. After the resin is poured, it is allowed to cure, often under specific temperature conditions. The cured resin parts are then removed from the mold and trimmed. Hand-finishing is a crucial step. This includes sanding, polishing, and applying paint. Details, such as decals and photo-etched parts, are then added. The resin model is often assembled by hand. The process is more labor-intensive than die-casting, resulting in lower production volumes. This is common for limited edition or custom models. This process enables modelers to create highly accurate and detailed models. The careful application of paint, decals, and other finishing details is critical to the final appearance of resin cars.
Diecast vs Resin Cars Detailing and Accuracy
Detailing and accuracy are crucial aspects for collectors and enthusiasts. Both diecast and resin models offer different strengths and weaknesses. The construction methods employed significantly impact the level of detail achievable. The level of accuracy determines how well the model represents the real-life vehicle. The ability to replicate the details of the original vehicle is highly sought after by collectors. It is important to consider the visual aspects of the model’s accuracy.
Diecast Detailing Advantages
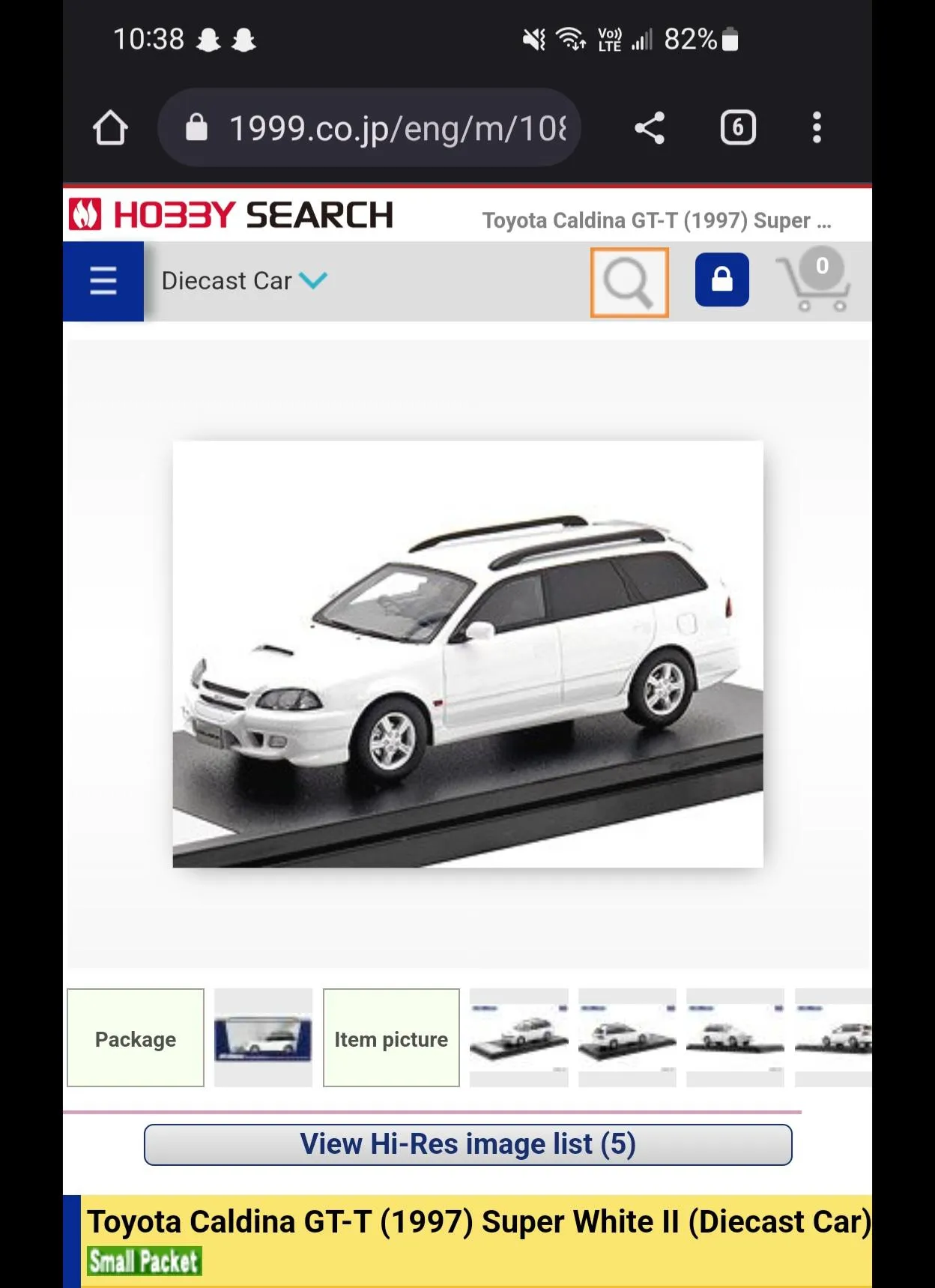
Diecast models have traditionally excelled in offering functionality and robust detailing. The die-casting process allows for the creation of working features, such as opening doors, hoods, and trunks. This is a significant advantage for collectors who appreciate interactive models. The detailing often includes realistic interiors, detailed engines, and accurate exterior markings. The use of tampo printing, a method that precisely applies paint, enables the creation of detailed logos and markings. Manufacturers can incorporate features that enhance the overall realism, such as steerable wheels. These features are not just for visual appeal, but they also provide a tactile experience. The materials used can also contribute to the overall level of detail and realism.
Resin Detailing Advantages
Resin models often focus on delivering extreme accuracy and intricate detailing. The mold-casting process allows for more complex shapes and fine details, such as intricate grilles, thin window frames, and delicate body lines. This level of detail is particularly appealing to enthusiasts who prioritize accuracy. The construction process often involves hand-finishing, which enables modelers to achieve a high level of precision. Resin models can incorporate photo-etched parts for exceptionally detailed components. These are not always possible with diecast models. Resin cars excel in representing specific vehicles, often limited editions, or racing cars. The ability to replicate complex curves and shapes makes resin an excellent choice for highly detailed replicas. These are a cornerstone of many high-end collections.
Diecast vs Resin Cars Durability and Weight
Durability and weight are essential considerations, especially for those who intend to handle and display their models regularly. The materials used and construction methods greatly influence these characteristics. The robustness of the materials directly impacts how well the model can withstand handling and environmental factors. The weight of the model can influence the tactile experience and the perceived quality of the model. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision on which model is best.
Durability Comparison

Diecast cars, with their metal bodies, are generally more durable and resistant to damage from impacts and handling. This makes them suitable for display and interaction, such as opening doors or rolling wheels. The robust construction of diecast models makes them more resistant to warping or deformation over time. They are better suited for environments where they might be exposed to changes in temperature or humidity. This makes them a practical choice for collectors. The die-casting process results in a solid construction that can withstand regular handling. Their robust nature makes them a practical choice for those looking for long-lasting models.
Weight Comparison
Diecast models, due to their metal construction, are significantly heavier than resin models. This added weight provides a satisfying tactile feel and enhances the sense of quality. The weight also contributes to the model’s stability, reducing the risk of it tipping over during display. The weight adds to the overall impression of realism and quality. Resin models, on the other hand, are generally lighter, offering a different tactile experience. However, this does not always equate to a lower-quality feel, as the detailing and accuracy can be exceptional.
Diecast vs Resin Cars Collectibility and Value
Collectibility and value are key factors for many enthusiasts. The popularity of model cars drives a market that is influenced by several factors. Understanding how these factors influence the value of these models is crucial for both new and experienced collectors. The value can be influenced by several factors. These factors vary depending on the model type.
Factors Influencing Collectibility

Rarity, detailing, and brand reputation significantly influence the collectibility of both diecast and resin cars. Limited edition models and those with exceptional detailing often command higher values. The brand of the model, its historical significance, and the accuracy of the replica also impact collectibility. The condition of the model is a critical factor; models in pristine condition are usually more valuable. Diecast models with working features and resin models with intricate detailing have high value. Popular models often increase in value over time due to demand. Factors such as historical accuracy and the overall aesthetic also influence a model’s collectibility and desirability.
Factors Influencing Value
Several factors affect the value of model cars. Rarity, including limited production runs, is a key driver of value. The accuracy and detailing of the model, as well as the brand’s reputation, play a significant role. The condition of the model, including the box and any accompanying documentation, is essential. Models that accurately represent historically significant vehicles often have higher values. The demand for a particular model within the collector community also influences its worth. Limited editions and those with exceptional detail often command a premium price. The brand’s legacy and the quality of materials used are essential in assessing the value of a model car.
Diecast vs Resin Cars Cost and Availability
Cost and availability are critical considerations for any collector. The manufacturing processes used for diecast and resin cars affect their price points and distribution. The production volume, the complexity of the manufacturing process, and the materials used all play a part in the cost and availability. Understanding these differences allows collectors to make informed purchasing decisions.
Price Comparison

Diecast cars are generally more affordable due to the mass production capabilities of the die-casting process. They are often accessible to a broader audience, making them a popular starting point for many collectors. Resin models tend to be more expensive. The higher price is due to the more labor-intensive production and limited production runs. The price difference reflects the production costs and the exclusivity associated with resin models. Diecast models offer an excellent entry point for collectors on a budget. Resin models typically appeal to those who are willing to pay a premium for higher detail and limited availability.
Availability Comparison
Diecast cars are widely available in various retail outlets, online stores, and hobby shops. The mass production process enables extensive distribution networks. This makes them easy to find and readily accessible to most collectors. Resin models are often produced in smaller quantities, making them less readily available. Resin models are typically available through specialist retailers, online platforms, and directly from manufacturers. Collectors looking for specific resin models often need to be more diligent in their search, as they may be limited editions. The exclusivity of resin models can be a significant appeal for collectors who seek unique pieces.
In conclusion, the choice between diecast and resin model cars depends on individual preferences and collecting goals. Diecast models are known for their durability, affordability, and detailed features, making them a great choice for many collectors. Resin models, with their emphasis on detail and accuracy, appeal to enthusiasts who appreciate the artistry. Both types provide a way to connect with the world of automobiles and the history of cars. Ultimately, the best model car is the one that brings you the most joy and satisfies your collecting passion.
